

eProcessor’s application in a nutshell
March 4, 2025


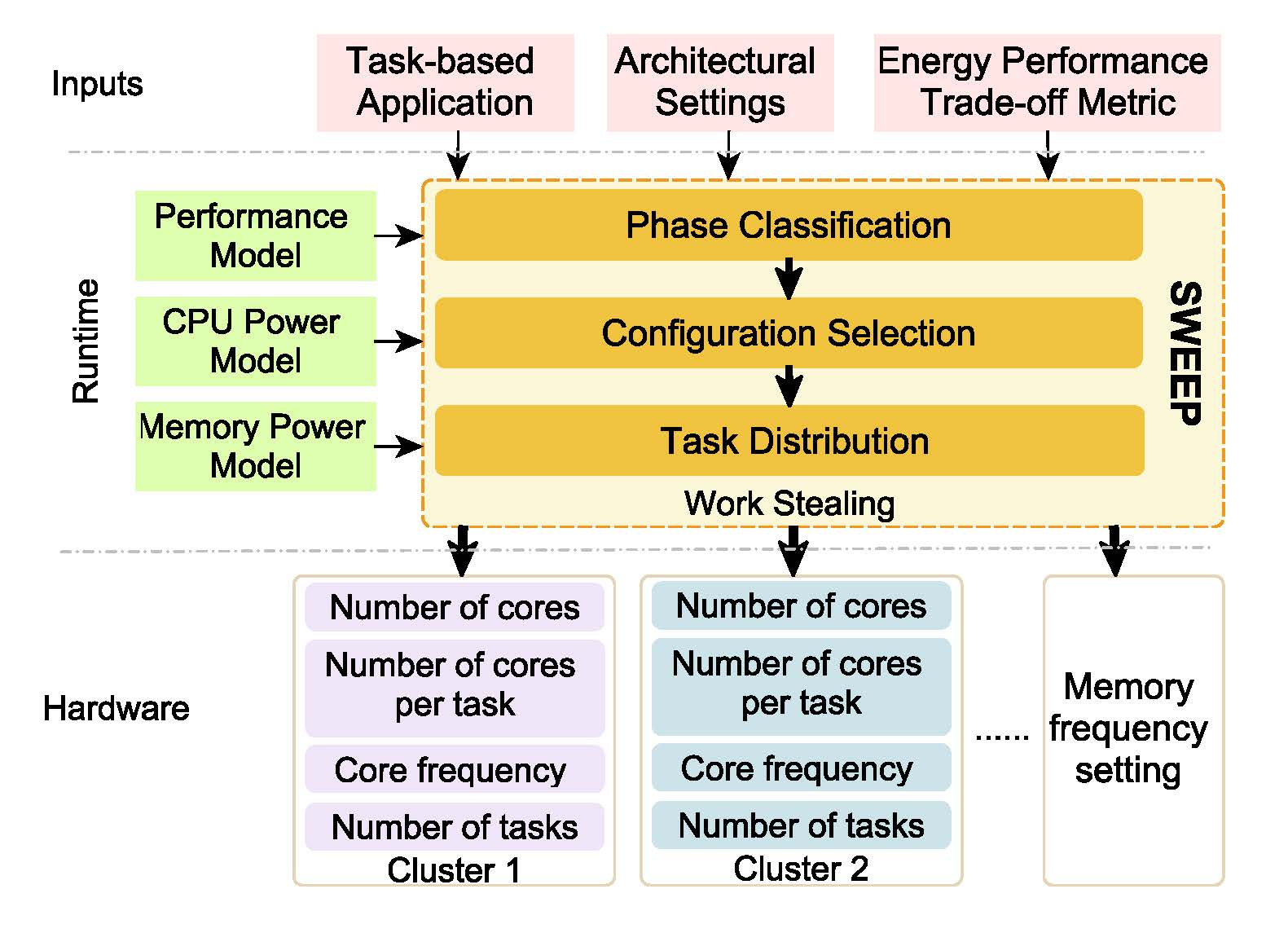
Task Scheduling in a nutshell
September 12, 2024
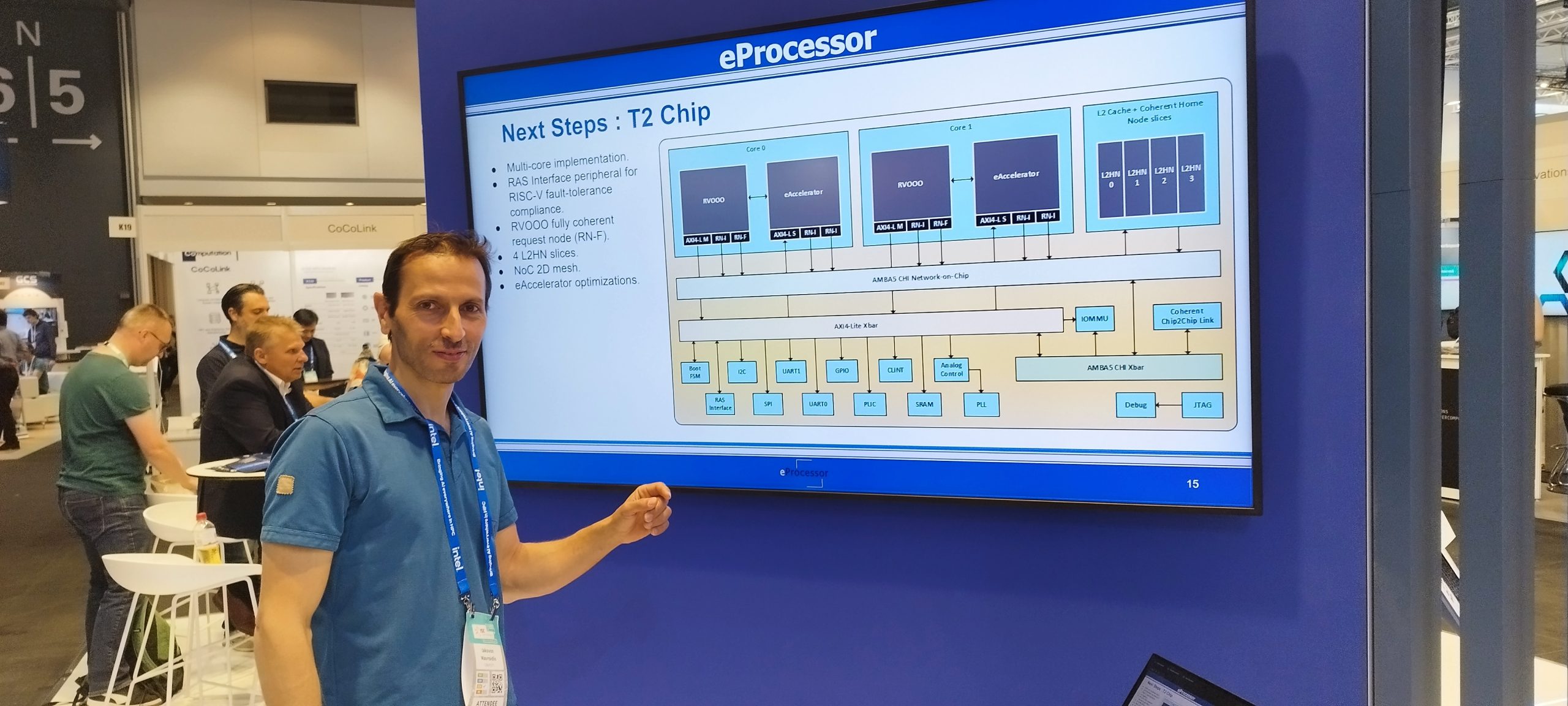
eProcessor is in ISC 2024
May 1, 2024
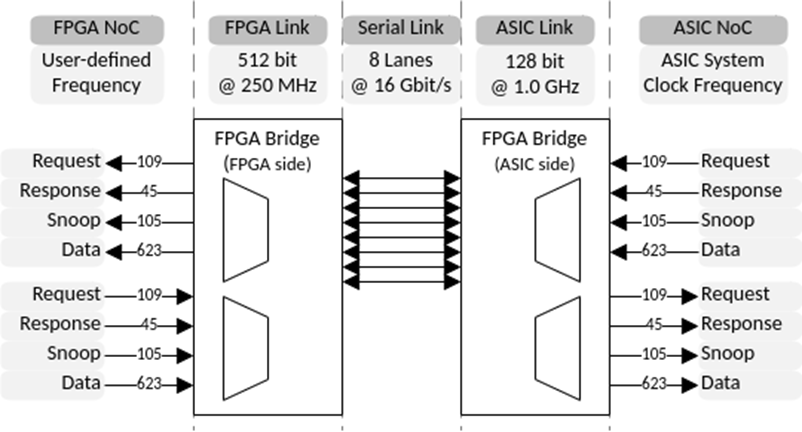
Chip-to-Chip (C2C) in a nutshell
February 23, 2024

eProcessor is in HiPEAC 2024
January 16, 2024








